RS485 is a popular industrial standard for serial communications. The Industruino IND.I/O has an RS485 port connected to the 'Serial' hardware serial (D0/D1).
Note that RS485 is half-duplex, so we cannot send and receive at the same time. We need to use a TxEnablePin to switch between sending and receiving. This pin is connected to D9 on our MCU.
We can use RS485 to communicated between 2 IND.I/Os: we simply have to connect 2 wires for the RS485: A to A, and B to B as in this example.
In the same way, we can also communicate with any Arduino, using a common RS485-to-Serial converter on the Arduino side, as we will describe here.
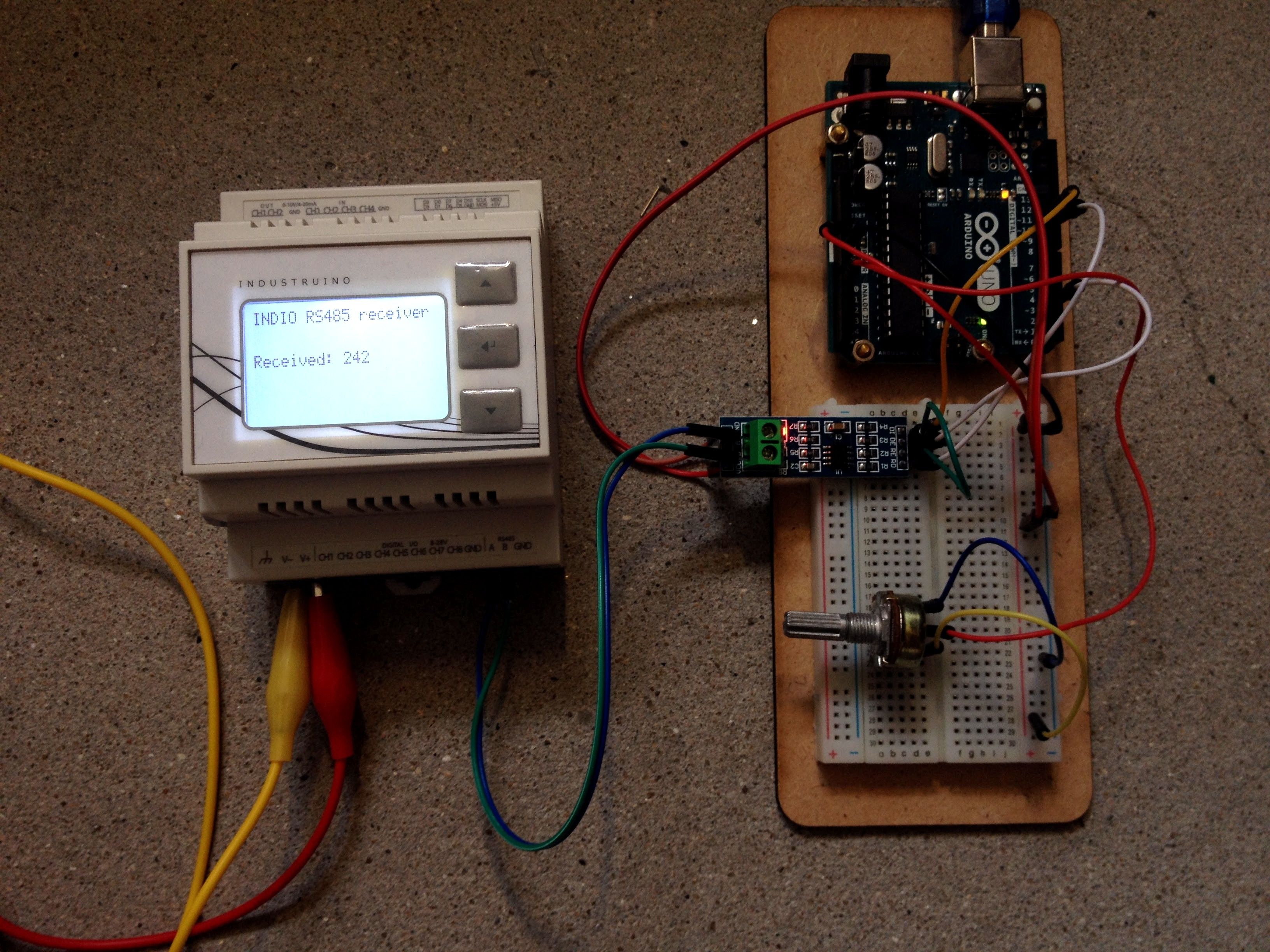
Notes on the below Industruino code:
- the TxEnablePin is D9
- the serial's name is 'Serial' (on the current D21G boards; on the older 32u4/1286 boards it was 'Serial1')
- it waits for input on Serial
- in case you want to use the Serial Monitor, use 'SerialUSB'
Notes on the Arduino code:
- this sketch uses a software serial (D10/D11), so that you can still use the hardware serial for the Serial Monitor
- it reads the value of analog input A0, and divides it by 4 for the range 0-255
- it writes this byte to the software serial
For more complex data exchanges, we recommend the Modbus RTU protocol, as in this example.
INDIO sketch (tested with D21G)
/*
* Industruino INDIO RS485 serial demo RECEIVER
* INDIO has a half duplex RS485 port connected to hardware Serial
* TxEnablePin is D9
*/
#include <UC1701.h>
static UC1701 lcd;
const int TxEnablePin = 9;
byte byte_received;
void setup() {
pinMode(26, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(26, HIGH); // LCD backlight
lcd.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(TxEnablePin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(TxEnablePin, LOW);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("INDIO RS485 receiver");
lcd.setCursor(0, 3);
lcd.print("Received:");
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) {
byte_received = Serial.read();
lcd.setCursor(60,3);
lcd.print(byte_received);
lcd.print(" ");
}
}
ARDUINO sketch (tested with Arduino UNO)
/*
* Industruino INDIO RS485 example communication with Arduino over RS485
* this sketch is for the Arduino: it sends the value of a potentiometer as a byte over RS485
* more info on RS485 for Arduino at https://arduino-info.wikispaces.com/SoftwareSerialRS485Example
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#define SSerialRX 10 //Serial Receive pin
#define SSerialTX 11 //Serial Transmit pin
#define SSerialTxControl 3 //RS485 Direction control
#define RS485Transmit HIGH
#define RS485Receive LOW
SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(SSerialRX, SSerialTX); // RX, TX
int byteSend;
void setup() {
pinMode(SSerialTxControl, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SSerialTxControl, RS485Receive); // Init Transceiver
RS485Serial.begin(9600); // set the data rate
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(SSerialTxControl, RS485Transmit);
RS485Serial.write(analogRead(A0)/4); // Send pot reading
delay(10);
digitalWrite(SSerialTxControl, RS485Receive); // Disable RS485 Transmit
delay(100);
}